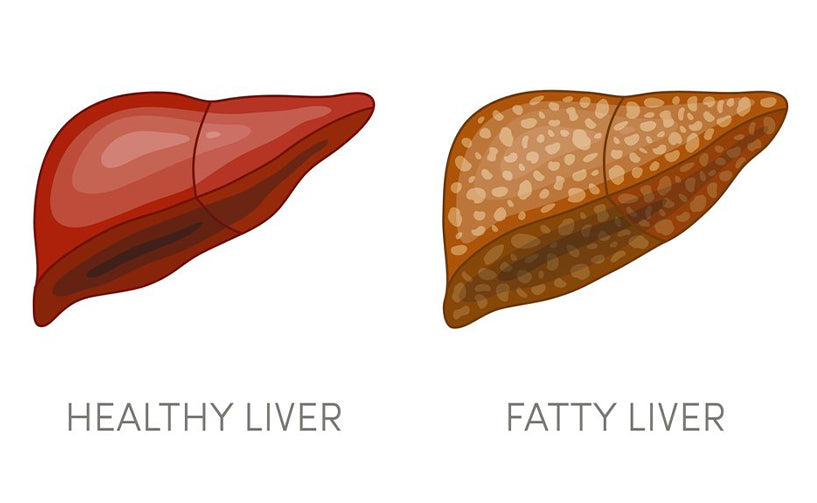
Too much fat in the liver is the sign of poor health. Fatty liver is the build-up fat or excess stored fat or accumulated large lipid molecules in the liver cells which hampers normal liver functions. It occurs when fat account for 5-10% or more of your livers weight. Since the main function of the liver is to process the food we eat and to filter out toxins from our body, any disruption may burden our health and may cause other health complications.
Fatty liver is a curable problem and often occurs without any symptoms. Heavy drinking or alcoholism is the main contributing factor towards fatty liver. Other important causes are hyperlipidaemia, obesity, family history, diabetes and certain allopathic medications. Normally, the liver repairs itself by building new cells when the old ones get damaged. But repeated damage can cause permanent scarring and the condition is called cirrhosis.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease or alcoholic steatohepatitis accompanied with inflammation may lead to cirrhosis and hepatitis. While non-alcoholic fatty liver doesn’t have any cell damage or inflammation and do not cause any further complications. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis which is another type of syndrome related to fatty liver, comes with inflammation, scarring and fibrosis which may lead to liver cancer and cirrhosis.
Fatty liver disease exists without any major symptoms so it is bit difficult to find out or identify. Minor symptoms like weight or appetite loss, abdominal pain, weakness etc. can exist. A physician may recommend liver tests including previous medical history and a physical examination.
Do’s
- Eat mineral and vitamin rich food
- Drink lots of water, at least 3-4 litres a day
- Exercise daily
- Reduce cholesterol and manage blood sugar
Don’ts
- Avoid unhealthy and extreme weight loss
- Avoid alcohol as it can cause severe damage
- Avoid processed foods
- Avoid medicines with compounds similar to aspirin, steroids, tamoxifen, and tetracycline